The global concrete industry is at a pivotal juncture of green transformation, digitalization, and international expansion. In 2023, the global market surpassed USD 450 billion, and over the next five years it is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5–7%, potentially exceeding USD 600 billion by 2030. Market expansion is being driven both by infrastructure demand in developing regions (e.g., Southeast Asia, Africa) and by renovation projects in advanced economies. At the same time, tightening environmental regulations, breakthroughs in low-carbon technologies, and regional market differentiation have become key variables shaping the industry’s trajectory. As the world’s largest single market, China is leveraging the Belt and Road Initiative to deepen its international footprint while simultaneously promoting an upgrade to green building materials and smart manufacturing.

This white paper synthesizes the latest global and regional data and trends in the concrete industry, focusing on market size, five-year outlook, critical technologies, environmental and sustainability innovations, competitive landscape, value-chain dynamics, and relevant policies and regulations.
Major Insights and Key Findings:
- Continued market expansion: Accelerated urbanization and rising infrastructure investment have sustained stable growth in the global concrete market. Over the next five years, the market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 3–5%, with the fastest growth in Southeast Asia, the CIS, Latin America, and Africa.
- Fusion of technological innovation and environmental performance: High-performance concrete, digital automation, and advanced process controls have become industry mainstreams. Concurrently, the development and deployment of energy-saving and green building materials are accelerating.
- Optimizing competitive dynamics: Leading firms are consolidating their positions through scale advantages and technological leadership. Emerging players are leveraging internet platforms, big data, and novel business models to compete, often resulting in collaborative, win-win partnerships.
- Stricter regulations driving transformation: Across all regions, environmental and safety standards are tightening. Evolving concrete industry certifications and norms provide a robust regulatory framework that supports enterprise upgrading.
- Opportunities paired with challenges: The industry is entering a golden age of structural optimization, smart manufacturing, and green development, yet must simultaneously manage raw-material price volatility and rising environmental compliance costs.
This white paper aims to provide concrete-industry stakeholders—manufacturers, investors, and policymakers—with a comprehensive, objective, and professional set of market insights and strategic recommendations.
Overview of the Concrete Industry
Market Analysis
Industry Market Size
The global concrete industry is currently in a phase of steady growth. Latest statistics show annual world production of nearly 6 billion cubic meters of concrete, with ready-mix concrete’s penetration rate continuing to rise in construction projects. China, as the world’s largest producer and consumer, has a market exceeding RMB 400 billion and is expected to maintain high activity levels in the coming years. Meanwhile, although growth in North America, Europe, and Japan is slower, demand for high-performance concrete in these advanced markets continues to climb steadily, resulting in an overall landscape defined by significant scale and diversified development.
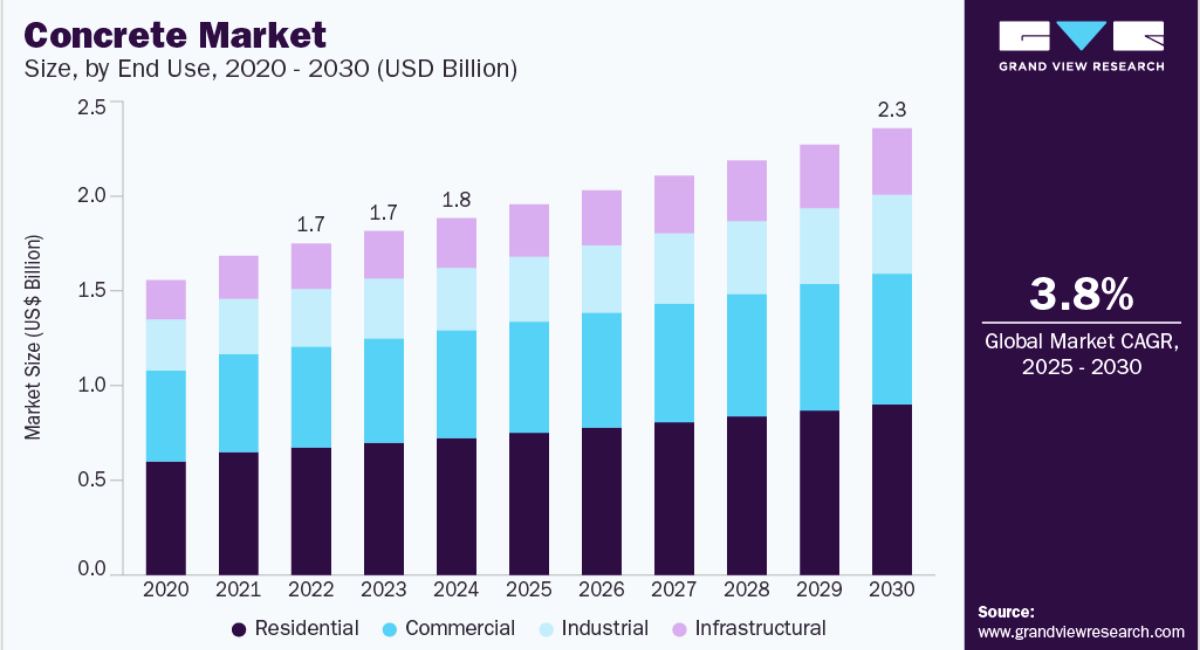
Five-Year Outlook
Over the next five years, the concrete industry is expected to exhibit the following trends:
- Scale growth coupled with structural upgrading: Accelerated urbanization, increased infrastructure investment, and the proliferation of green-building concepts will drive further market expansion. Concurrently, the focus will shift from purely high volumes toward enhanced product quality, environmental performance, and bespoke high-end solutions.
- Technology-driven transformation: Widespread adoption of digitalization, smart manufacturing, IoT integration, 3D printing, and automated production will accelerate industry upgrading, boost efficiency, improve product consistency, and ultimately enhance profit margins.
- Regulatory support for green transition: Governments worldwide are imposing stricter energy-use and carbon-emission requirements for construction materials. This is catalyzing R&D and application of low-carbon, eco-friendly concrete products, making green transformation an industry imperative.
- Supply-chain consolidation and rising concentration: Anticipated industry consolidation will leverage economies of scale. Leading enterprises will outcompete rivals through superior technology and brand strength, gradually increasing overall market concentration.
- Circular economy and resource efficiency: The use of recycled aggregates—transforming demolition waste such as old concrete and masonry into sand and gravel substitutes—will significantly reduce natural resource extraction and CO₂ emissions.
Regional Market Analysis

Southeast Asia
Rapid economic growth and strong infrastructure investment have created tremendous potential in the Southeast Asian concrete market, particularly in urban renewal and transport projects. However, the region also faces mounting environmental‐compliance challenges.
Growth drivers:
- Urbanization rate increases (e.g., Indonesia, Vietnam)
- Major transport investments (e.g., Thailand high‐speed rail, Philippine port expansions)
- Projected annual concrete‐demand growth of 8–10%
CIS (Commonwealth of Independent States)
Resource wealth is high, but equipment and technical capabilities vary widely. Over time, technology transfer and joint ventures are expected to drive industry upgrading in select countries.
- Key markets: Russia and Kazakhstan, where energy‐sector infrastructure (e.g., oil & gas pipelines) underpins strong concrete demand
- Entry strategy: Chinese firms expanding via local joint‐venture partnerships
Latin America
Infrastructure and housing construction are the main growth engines, producing stable demand—though macroeconomic volatility can introduce uncertainty.
- Notable projects: Brazil and Mexico’s major initiatives, such as Mexico’s Maya Train
- Market trend: Demand growth is healthy but susceptible to economic cycles, leading to uneven year‐to‐year performance
Africa
Demographic dividends and rapid urbanization present significant opportunities. Governments have increased infrastructure spending, which should drive fast concrete‐demand growth, though technology adoption and environmental‐regulation enforcement remain challenges.
- High‐potential markets: Nigeria and Kenya, where urbanization is low but accelerating
- Outlook: Projected CAGR of 12% from 2025 to 2030
Europe
A mature market with deep commitment to sustainability and green building. Demand for high‐quality, low‐carbon concrete continues to rise as automation and digitalized production become mainstream.
- Policy impetus: EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) pressures industry to lower emissions; Germany and France promoting low‐carbon certification standards (e.g., LEED)
- Green penetration: Green‐certified concrete expected to exceed 30% of total market by 2025
North America
Steady market expansion—especially driven by infrastructure renewal and energy‐efficiency mandates—is pushing the industry toward higher efficiency and lower carbon intensity. The U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act has released over USD 1 trillion for bridges, highways, public transit, and clean‐energy projects, raising the bar for high‐performance concrete and automated production equipment. Competitive differentiation is increasingly based on technological innovation, smart upgrades, and integration with green‐certification systems.
Growth drivers:
- Aging infrastructure (≈47,000 U.S. bridges in need of repair)
- Environmental legislation boosting green‐building material adoption
- Industry growth rate of 5–7% annually
- Rising interest in automated batching plants, intelligent dispatch systems, and carbon‐capture cement technologies
Middle East
Energy revenues are fueling frequent, large‐scale infrastructure and urban‐development projects. National initiatives—such as Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 and the UAE’s Expo‐2020 legacy programs—have significantly increased demand for concrete equipment and advanced materials. Extreme climate conditions (high heat, aridity) place higher performance requirements on concrete, driving widespread use of heat-resistant, sulfate-resistant mixes and high-performance admixtures.
Growth drivers:
- Major strategic investments (e.g., NEOM in Saudi Arabia, post-World Cup legacy conversions in Qatar)
- Stable annual concrete‐demand growth of 6–8%
- Heightened requirements for centralized, smart ready-mix production in the UAE and Qatar
Oceania
Centered on Australia and New Zealand, Oceania’s concrete sector is transitioning toward green and intelligent production under the combined pressures of infrastructure upgrading and stricter environmental regulations. Demand for remote-site construction—particularly roads and resource-sector projects—has driven widespread adoption of compact, portable batching plants. Sustained government infrastructure spending and a resilient property market underpin stable market growth.
Growth drivers:
- AUD 120 billion infrastructure plan over five years by the Australian federal government
- New Zealand’s Infrastructure Upgrade Programme for urban drainage, roads, and bridges
- Environmental regulations driving rapid uptake of green concrete and sustainable building materials, with green products expected to account for 35% of the market by 2025
Future Five-Year Trends
Looking ahead, the global concrete industry will be propelled by three overarching themes: greening, digitization, and globalization. Infrastructure demand in emerging economies (Southeast Asia, Africa) and low-carbon transitions in developed regions (Europe, North America) will jointly drive growth. Companies must pay close attention to policy signals (e.g., carbon pricing), breakthrough technologies (e.g., CCUS), and region-specific market strategies.
Technology Trends
Key Technology Developments
Concrete production is accelerating its shift from traditional methods toward greener, smarter, automated, and digitalized processes. Notable advancements include:

Green, Low-Carbon Technologies
Green Low-Carbon Technologies: Carbon Neutrality-Driven Disruptive Innovation
Scaled Use of Recycled Aggregates (RCA): The replacement rate of recycled construction waste (e.g., demolished concrete and masonry) is projected to rise from 28% in 2023 to 45% by 2030. Innovations such as microwave activation and nano-silica modification are resolving strength and water-absorption trade-offs. The China Academy of Building Research’s “micropowder activation” technique has achieved C50 compressive strengths in RCA concrete while reducing costs by 30%.
Breakthroughs in Low-carbon Binders: Commercialization of calcium-carbonate concrete (CCC) and alkali-activated slag cement (AAM) has cut CO₂ emissions by 60–80% versus Portland cement. The University of Science and Technology Beijing’s CO₂ mineral-curing method, deployed in Xiong’an New Area, reduces lifecycle carbon footprints by 21 kg/m³ of concrete.
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS): Germany’s Heidelberg launched the world’s first CCUS system on a concrete kiln, sequestering 100,000 tonnes of CO₂ annually. In China, CNBM and Conch Cement are advancing “calcium carbide slag substitution” technology to lower clinker emissions below 350 kg CO₂/ton.
Automation and Digital Monitoring
Programmable logic controllers (PLC), human-machine interfaces (HMI), IoT sensors, and big-data analytics now enable full-process oversight of mix proportions and mixing cycles—significantly enhancing product consistency and plant throughput.
Intelligent and Digitalization: Revolutionizing End-to-End Process Efficiency
AI-driven Mix Optimization: AI ratio-design models (e.g., those from CSCEC West Construction) have cut cement usage by 12–15% while controlling compressive-strength variability within ±1.5 MPa.
IoT and Digital-twin Applications: Approximately 60% of leading producers employ IoT monitoring to optimize energy use and quality in real time. Glodon’s BIM quantity-takeoff software—holding 41% market share—integrates design-to-construction workflows and slashes settlement cycles by 40%.
Predictive Maintenance & Quality Traceability: Machine-learning–based failure-prediction systems reduce unplanned downtime by 40%. Blockchain platforms are now enabling full-chain traceability of ready-mix quality under newly drafted industry standards.
High-Performance Concrete Mix Design
Ultra-high-performance Concrete (UHPC): With compressive strengths exceeding 200 MPa, UHPC is being used in Saudi Arabia’s NEOM skyscrapers and Shanghai’s sinkhole-site hotel. Ningbo Zhongchun Hi-Tech’s automated welding equipment has driven down UHPC precast-pile costs by 25%.
Self-healing and Responsive Materials: Technologies such as bacteria-encapsulated spores and shape-memory polymers (SMPs) enable crack closure, extending service life by over 20 years. The Chinese Academy of Sciences’ phase-change materials (PCM) in concrete can reduce building energy loads by 30%.
Nanomaterial Enhancers: Carbon nanotubes and nano-silica additions increase concrete impermeability by 50%. The China Academy of Building Research’s nano-concrete has been applied to anti-corrosion works on the Hong Kong–Zhuhai–Macau Bridge.
3D Printing and Intelligent Construction Technologies
3D Printing & Industrialized Construction Disrupting Traditional Methods
3D-Printed Building Components: In several advanced economies, pilot projects are already underway for 3D printing entire concrete structures. Suzhou Kunlun Green Building Technology achieves a daily print volume of 20 m³—reducing costs by 30% compared to conventional methods. Shanghai Construction Group has demonstrated 24-hour printing of a 200 m² residential unit with dimensional tolerances under 2 mm.
Prefabricated Modular Systems: The fully prefabricated UHPC-reinforced concrete (UHPC-RC) segmental girder technology, honored with a National Science and Technology Progress Award, cuts on-site wet work by 80% and reduces overall construction time by 50%.
Intelligent Construction Equipment:
- CIMC & Shaanxi Auto’s hybrid mixer truck integrates a photovoltaic power system, extending operational range by 40%.
- Beijing Yugou’s AI inspection robot performs three-dimensional measurement of tunnel segments with 0.1 mm accuracy.
Circular Economy & Resource Recycling: Building a Closed-Loop Value Chain
Deep Utilization of Industrial By-Products: Incorporation rates of steel slag and fly ash have risen to 30%, enabling CNBM (China National Building Material Group) to process over 100 million tonnes of industrial waste annually. Electric-drive mixer trucks now account for 40% of new sales, and by 2030 photovoltaic-powered batching plants are projected to represent 60% of installations.
Full-Component Recycling of Construction Waste: A Shanghai industrial park processes 10 million tonnes of demolition debris per year. Recycled aggregates are repurposed for permeable pavements and subgrade fill, achieving a resource-recovery rate exceeding 90%.
Carbon Credits & Green Finance: According to Minsheng Securities, under ESG investment frameworks concrete producers will issue over CNY 30 billion in green bonds by 2025—offering yields 11.5 percentage points below conventional corporate debt.
Environmental Protection & Sustainability Technologies
Low-Carbon Concrete and Recycled AggregatesBy leveraging nanomaterials (e.g., carbon nanotubes), high-efficiency water-reducing admixtures, low-carbon cements, industrial by-products (fly ash, slag powder, steel slag), and recycled aggregates, producers can substantially lower concrete’s carbon footprint—advancing green‐building objectives.
Energy-Saving Equipment & Process OptimizationAdoption of renewable energy sources, waste‐heat recovery systems, and high-efficiency mixers enhances energy utilization while reducing CO₂ emissions. Intelligent process control enables real-time optimization of both energy consumption and product quality. Early-stage mix‐design optimization further minimizes on-site waste.
Wastewater Treatment & Reuse SystemsIntegration of sand-gravel separators and multi‐stage settling pools enables 100% wastewater recycling. Comprehensive collection, purification, and reuse infrastructures control pollutant discharge and dramatically cut fresh‐water demand.
Technology Suppliers and R&D Trends
Global suppliers in the concrete sector are markedly increasing R&D investment to drive both technological innovation and industry upgrading.
Intelligent & Digital Technology Suppliers
Smart Construction Control Systems
- Siemens (Germany): Leads the industry in programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and automated pumping solutions, offering unmatched programming stability.
- Huawei (China): In partnership with CSCEC West Construction, has developed a BIM + 5G collaboration platform that reduces design-change time by 30%.
- HBC Radiomatic (Germany): Provides wireless remote-control systems for precise boom-arm manipulation on concrete pumps, streamlining operator workflows.
IoT & Data Analytics
- SAP (Germany): Their supply-chain management suite optimizes the entire concrete production-transport-placement cycle, improving inventory turnover by 25%.
- Glodon (China): Commands 41% of the BIM quantity-takeoff software market, automating material calculations and cost control.
Construction Technology & Green-Tech Suppliers
- MX3D (Netherlands): Pioneer of recycled-aggregate 3D-printed bridge components, cutting material waste by 60% and costs by 30%.
- Shanghai Construction Group (China): Developer of UHPC-RC segmental girder technology, which halves construction time and earned a National Science & Technology Progress Award.
Green Technology Solutions Provider
- Heidelberg Materials (formerly LafargeHolcim): Leader in carbon-capture utilization and storage (CCUS), sequestering over 500,000 tonnes of CO₂ per year.
- VICON (Netherlands): Uses nanotechnology to reformulate concrete, incorporating 50% industrial by-products and boosting compressive strength by 20%.
R&D Trends
Over the next five years, R&D in the concrete industry will evolve from isolated material improvements to a three-pillar strategy of greening, digitalization, and functionalization:
- Scaled Recycled-Aggregate Adoption: From pilot to mass deployment, driven by activation and modification technologies.
- Commercialization of Self-Healing Materials: Biocapsules and shape-memory polymers moving from lab to field.
- AI-Powered Smart Production: End-to-end automation—mix-design, process control, and predictive maintenance.
Policy drivers (e.g., carbon border adjustments) and market demands (e.g., offshore infrastructure) will accelerate technology cycles. To lead tomorrow’s market, companies must pursue cross-value-chain collaboration, capturing first-mover advantages in the low-carbon, digitalized economy.
Competitive Landscape and Industry Value Chain for the Concrete Sector
Competitive Players
Leading Multinationals
LafargeHolcim
- The world’s largest cement and concrete producer, with operations in over 150 countries.
- Growth driven by strategic mergers and acquisitions that enhance scale and optimize supply-chain integration.
- Aggressively expanding its “green, low-carbon” portfolio, including the LC³ limestone-calcined clay cement and low-carbon blended concretes.
HeidelbergCement
- Europe’s market leader, with strong positions in North America and Asia.
- Investing heavily in digitalized plants and smart production lines.
- Deploys platforms akin to “CEMEX Go” to streamline order management, logistics, and overall operational efficiency.
China National Building Material Group (CNBM)
- The largest concrete producer globally by capacity and output. In 2024, CNBM’s total concrete production exceeded 500 million m³, representing roughly 15 percent of China’s market.
- Ready-mix capacity stands at 78 million m³, with facilities in all 31 provinces and joint-venture or wholly owned plants in 12 Belt-and-Road countries.
Emerging Competitors
Digital & Platform Service Providers
- Domestic platforms such as Lagou Mixing Cloud and Gongdi e-Jia deliver end-to-end SaaS: online ordering, fleet dispatch, and quality monitoring.
- They partner with major concrete producers in “platform + plant” models, accelerating their digital transformation.
Precast & Modular Construction Firms
- Companies like China State Construction’s Huate nv and France’s Bouygues Construction subsidiary manufacture factory-made precast elements, reducing on-site casting.
- Their “off-site prefabrication + on-site assembly” approach enhances build quality, speed, and safety.
Green-Material Innovators
- Specialists such as Solidia (USA) and Calera (Netherlands) focus on carbon-capture cements; Hebei Anyin produces steel-fiber–reinforced low-carbon mixes.
- They collaborate with traditional cement makers to deliver custom low-carbon concrete solutions.
Smart Construction Technology Providers
- Shanghai Faxin Investment Holding offers integrated smart-plant control systems.
- Boleido pioneers 3D-printed concrete components for bridges and buildings.
Sustainable Concrete Service Firms
- Yunnan Construction Investment Concrete recycles aggregates from demolition waste.
- Shanghai Shenkun Qingsong operates unmanned testing laboratories to verify green-concrete performance.
Partnership Models
To drive innovation, manage risk and expand market reach, industry players are adopting a variety of collaborative structures:
Multinational & Local Joint Ventures
Rationale: Combine global technology leadership with local market knowledge to mitigate regulatory and political risk.
Examples:
- LafargeHolcim & CSCEC West Construction: Established a high-performance concrete R&D center that brings European self-healing concrete technology to Belt & Road projects.
- Conch Cement & West Construction: Through a directed share issuance, Conch secured strategic investment from West Construction, sharing supply-chain and customer networks and boosting concrete capacity by 25% in three years.
Industry Alliances & Consortia
Rationale: Lead firms partner with upstream raw-material suppliers (mines, chemical producers) to co-develop new materials and standardized mix designs.
Example: LafargeHolcim’s global collaboration with Sika on high-performance supplementary cementitious materials.
Vertical Supply-Chain Integration
Rationale: End-to-end cooperation—from raw-material extraction through production and construction—allows companies to secure feedstock and lock in downstream demand.
Example: CNBM and HeidelbergCement jointly invested in aggregate mines that process over 1 billion tonnes per year, reducing feedstock costs by 20%.
Deep OEM–Producer Partnerships
Rationale: Equipment manufacturers customize technology and provide integrated after-sales support, maximizing plant efficiency.
Example: Zoomlion and CSCEC TCC co-developed an AI-driven batching plant that optimizes mix parameters in real time, cutting cement use by 12% and energy consumption by 15%.
Industry–Academia–Research Collaboration
Rationale: Joint innovation centers with universities and research institutes tackle frontier topics such as ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) and self-consolidating concrete (SCC).
Example: HeidelbergCement’s partnership with Germany’s Fraunhofer Institutes to develop energy-saving and emission-reduction technologies.
Cross-Border M&A & Regional JVs
Rationale: Acquiring local mid-sized producers or forming joint ventures with state-owned enterprises accelerates market entry in emerging regions.
Examples:
- Anhui Conch’s joint venture projects across Southeast Asia.
- CRH’s acquisitions of paving and mixing businesses in North America.
Joint R&D & Patent Pooling
Rationale: Sharing R&D costs and intellectual property reduces development expense and accelerates technology adoption.
Example: The European Concrete Association (ECA) facilitates member-company cooperation on low-carbon concrete, lowering carbon-capture costs by 30%.
Future Collaboration Trends
- “Technology + Capital” Dual Engines: Partnerships that combine deep technical expertise with financial resources.
- Platform-Based Ecosystems: Digital platforms that connect producers, suppliers and service providers in a shared ecosystem.
- ESG-Driven Alliances: Collaborations explicitly designed to meet Environmental, Social and Governance criteria and access green finance.
Industry Value-Chain and Value Distribution
The concrete industry value-chain can be segmented into upstream raw-material supply, midstream production, downstream application markets, and auxiliary service sectors. Its value distribution follows a “smile curve”: low value-add upstream, high concentration midstream, and differentiated premiums downstream.
Upstream: Raw-Material Supply (≈25–30% of Value)
This segment supplies the fundamental inputs for concrete production.
Cement (35–40% of input cost): Excess capacity and environmental controls cap selling prices; typical gross margins are only 10–15%.
Sand & Aggregate (≈30% of cost): Depletion of natural sand has driven machine-made sand to 65% of total usage, but regional transport costs remain volatile.
Industrial By-products: Incorporating steel slag and fly ash at a 28% rate lowers cement demand while commanding an environmental premium.
Value Characteristics
- Thin Margins: Raw-material prices fluctuate sharply (e.g., 8% cement price decline in 2024), and investments in pollution controls (e.g., desulfurization upgrades) can consume 2% of revenues.
- Resource Leverage: Leading producers secure mine ownership (e.g., CNBM controls over 10 billion tonnes of limestone), strengthening bargaining power.
Midstream: Production & Manufacturing (≈45–50% of Value)
This core segment transforms inputs into ready-mix concrete, typically via dedicated batching plants or on-site mixers.
Batching Plants (≈60% of industry output value): Smart “lighthouse” plants (e.g., Sany’s automated facility) reduce unit costs by RMB 13/m³ and achieve 29.7% gross margins.
Green Technologies: Processes such as CO₂-mineral curing can cut per-cubic-meter emissions by 21 kg, yielding a 15% price premium.
Value Characteristics
- Scale Economies: Top 10 firms account for 31.3% of capacity, achieving 18% lower costs per unit than smaller operators.
- High Technical Barriers: R&D for UHPC exceeds RMB 100 million, with licensing fees of 5–8% of sales.
Downstream: Application Markets (≈25–30% of Value)
This final stage realizes the product’s value in a wide range of infrastructure, building, and specialty projects.
Infrastructure (43% of demand): High-strength mixes (C60+) for bridges and high-speed rail command 20–30% premiums.
Real Estate (35% of demand): Precast concrete for modular construction yields 25% margins—double that of traditional cast-in-place concrete (12%).
Value Characteristics
- Segmented Pricing: Marine-grade concretes (e.g., for offshore islands) can cost three times standard mixes but require specialized expertise.
- Price Sensitivity: Regional oversupply can spark price wars (e.g., North China’s C30 mix fell 7% in 2024), squeezing margins.
Auxiliary Services (≈10–15% of Value)
Smart Logistics: IoT-driven dispatch cuts transport losses to 1.5% and boosts efficiency 35%; logistics services represent 40% of this segment’s value.
Carbon-Asset Management: Carbon-trading and offset services yield >40% gross margins but depend on policy incentives.
Value Characteristics
- High Growth Potential: Digital delivery platforms (e.g., Glodon BIM) have 41% penetration and drive 20% annual service-revenue growth.
- Asset-Light Models: Equipment-leasing firms (e.g., Liebherr) combine “hardware + tech” services to achieve 18% ROE—well above manufacturing averages.
Concrete’s value-chain “smile curve” underscores that upstream raw materials offer limited profits, midstream manufacturing—through scale and technology—captures core value, and downstream applications realize premium pricing. Going forward, breakthroughs in green technologies (e.g., CCUS) and digital services (e.g., smart logistics) will be the new engines of value growth, propelling the industry toward higher-end, service-oriented models.

Policies and Regulations
Concrete Industry Policies and Regulations
Infrastructure-Driven Policies
Concrete demand has a high positive correlation with public infrastructure investment. In recent years, governments worldwide have treated infrastructure spending as a key economic stimulus, creating long-term growth momentum for the concrete sector.
| Country/Region | Policy | Description |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) | Allocates USD 1.2 trillion for bridges, highways, water systems, and power grids—boosting ready-mix concrete demand. |
| China | 14th Five-Year Plan | Focuses on urbanization, transportation power, and smart-city initiatives—driving large-scale concrete usage. |
| European Union | Recovery and Resilience Facility | Prioritizes green transport and infrastructure—providing funding for low-carbon, high-performance concrete projects. |
| Middle East | Saudi Vision 2030 & UAE 2050 Clean Energy Strategy | Supports major urban developments and industrial parks—demanding high-temperature-resistant and high-strength concrete. |
| India | National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) | Projects USD 1.5 trillion in infrastructure investment—ensuring sustained demand for ready-mix concrete. |
Concrete-Specific Policy Measures
To implement “green efficiency and smart-driven” industry goals, many governments have introduced targeted measures—regulatory, fiscal, and technical—to accelerate the concrete industry’s transformation and upgrade:
Mandating Ready-Mix Concrete over On-Site Mixing
Policy Tools:
- Designate ready-mix concrete as compulsory material for public and large-scale civil projects.
- Subject on-site mixing projects to dual “environmental and quality” assessments and incorporate compliance into bidding qualifications.
Support Measures:
- Subsidies or tax breaks for construction and operation of batching plants.
- Preferential procurement of locally certified ready-mix to support domestic producers.
Example:
- Berlin’s Green Construction Guidelines require 100% of municipal roads and bridges to use third-party–certified ready-mix concrete.
- Select Chinese provinces have blacklisted on-site mixing projects and imposed time-bound rectification orders.
Promoting Prefabrication and Modular Construction
Policy Tools:
- Include prefabricated building completion area in national “new industrialized building” targets.
- Offer land-use incentives and early payment to developers who meet prefabrication ratios.
Support Measures:
- Establish dedicated funds for pilot prefabrication parks, supporting automation and smart upgrades of production lines.
- Issue standardized design and quality-inspection guidelines for modular components.
Example:
- The U.K.’s Prefabrication Strategy established a £200 million industry fund to raise the prefabrication rate in housing and public buildings to 30%.
- Singapore’s Building Innovation Pilot Programme offers up to 20% project subsidies for factory-produced modular buildings.
Upgrading Small-Scale Batching Plants to Green, Intelligent Facilities
Policy Tools:
- Revise environmental and safety entry standards to require new or retrofit plants to install online monitoring, dust-control systems, and wastewater-recycling equipment.
- Prioritize “14th Five-Year” special funds for small-enterprise technology upgrades.
Support Measures:
- Publish a “Green & Intelligent Batching Plant Technical Guide” to facilitate automation, remote diagnostics, and big-data platform integration.
- Award “Green Factory” certification and credit incentives to plants that complete approved upgrades.
Example:
- Japanese municipalities subsidize 30–50% of costs for small plants installing dust-control, rainwater harvesting, and PLC automation systems.
- Canadian provinces pilot “smart construction” initiatives linking local emergency and environmental regulators with upgraded batching plants.
Environmental Regulations
The concrete industry is a major source of CO₂ emissions, energy consumption, and airborne dust, making it a primary focus of global environmental policymaking. Regulatory regimes are tightening worldwide, driving the sector toward lower-carbon, cleaner production.
Emissions Control Regulations
EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM): From 2026, imported cement and concrete products will attract a carbon levy, affecting exporting countries such as China and Turkey.
U.S. EPA Air Emissions Standards: Sets strict particulate‐matter limits for concrete batching plants and mandates installation of dust‐collection systems.
China’s Cement Industry Carbon Peak Implementation Plan: Requires coordinated energy‐efficiency improvements and carbon‐reduction measures across cement and concrete producers.
India’s Environmental Protection Laws: Enforce noise, wastewater, and dust limits for concrete plants under a local permitting regime.
Australia’s Clean Air Act: Requires batching sites to install dust‐capture and water‐recycling systems to control fugitive emissions.
Green Building Materials & Resource-Circulation Policies
Many governments now require green‐building‐materials certification for public‐sector tenders.
Incentives promote use of recycled aggregates and low-carbon cements (e.g., LC³) to close the material loop.
Subsidies, increased floor-area ratios, and energy-savings awards reward low-carbon concrete projects.
Jurisdictions are phasing out plants without environmental controls, mandating “smart + green” production lines.
Industry Standards & Certification Framework
With global market integration and the internationalization of construction projects, the concrete industry is rapidly aligning with worldwide standards, fostering transparent, certified, and green product and plant practices.
Principal Technical Standard Systems
| Standard | Issuing Body | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 22965 | ISO | Terminology, performance requirements, and factory control for ready-mix concrete |
| EN 206 | European Committee for Standardization (CEN) | Concrete classification, mix design, durability, and consistency |
| ASTM C94 | ASTM International | Specifications for ready-mixed concrete delivery, inspection, and control procedures |
| GB/T 14902 | Standardization Administration of China | Production quality and construction practices for ready-mix concrete |
| AS 1379 | Standards Australia | Quality management and third-party testing requirements for concrete |
Green-Material & Carbon-Footprint Certifications
| Certification | Region | Primary Focus |
|---|---|---|
| LEED | North America | Environmental performance and resource-efficiency ratings of concrete within building projects |
| BREEAM | United Kingdom | Life-cycle environmental impact assessment for building materials |
| China Green-Material Label | China | Star-rating system guiding procurement of certified green building materials |
| EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) | Global | Transparent disclosure of product carbon footprints to support international project bids |
Plant & Operational Management Certifications
- ISO 9001: Quality-management system for standardized plant processes.
- ISO 14001: Environmental-management system ensuring regulatory compliance.
- ISO 45001: Occupational health and safety standard for plant operations.
- CE Marking: Mandatory for concrete-equipment entering the EU market.
- Regional Low-Carbon Building-Material Certifications: For example, local green-material evaluation schemes in China used to score government tenders.
Opportunities and Challenges in the Concrete Industry

Opportunities
As global infrastructure investment, urban renewal initiatives, and green‐building principles gain momentum, the concrete sector is presented with unprecedented growth avenues:
Sustained Market Expansion
Infrastructure build-out and urbanization continue to accelerate worldwide. According to the International Cement Association, the global concrete market is projected to grow at a 3–4% CAGR over the next five years. In China, driven by new-type urbanization and large-scale renovation projects, the ready-mix segment is expected to expand at 6–7% annually. This backdrop offers concrete producers ample room to broaden their market footprint.
Digital and Smart Transformation
Automation, IoT, and big-data analytics are increasingly embedded in concrete production. Deploying digital management platforms and “smart factory” solutions can dramatically boost output efficiency, reduce material waste, and lower energy consumption. The China Building Materials Federation reports that intelligent equipment now penetrates over 45% of newly commissioned ready mix plants—creating a powerful lever to cut costs and improve batch‐to‐batch consistency.
Policy Support for Green and Low-Carbon Products
To advance low-carbon growth and sustainable construction, governments worldwide are rolling out financial incentives, tax credits, and procurement preferences for eco-friendly concrete and green building materials. Through targeted R&D and process upgrades, companies can capture these policy dividends and strengthen their competitive position.
Technological Innovation and Cross-Sector Collaboration
Breakthroughs such as self-compacting concrete, high-performance mixtures, and 3D‐printed structures are emerging from both industry and academia. These technologies not only enhance durability, aesthetics, and precision but also enable tailored solutions for complex projects. Meanwhile, transdisciplinary partnerships—particularly between universities, research institutes, and industry—are unlocking new pathways for process innovation and supply‐chain integration.
Challenges
Despite these tailwinds, the concrete industry faces a set of persistent obstacles:
Raw-Material Price Volatility
Cement, sand, and aggregates account for a large share of production costs, with cement alone representing up to 40% of total inputs. Tighter environmental controls and supply-chain constraints have driven pronounced price swings, squeezing producers’ margins.
Technology Barriers and Talent Shortages
Although digital and automated technologies are on the rise, many small and mid-sized enterprises lack the capital or expertise to adopt advanced systems. A dearth of engineers and operators skilled in smart-plant tools and data analytics further limits the pace of technology diffusion.
Environmental and Regulatory Pressures
Stringent air-quality, wastewater, and carbon-emission standards (e.g., under the U.S. Clean Air Act, China’s Pollution Prevention Law, and the EU’s CBAM) compel firms to upgrade pollution-control equipment and refine production processes—entailing significant CAPEX and higher operating costs.
Intensifying Market Competition
Leading global and regional players leverage superior technology, brand recognition, and integrated supply chains to dominate key markets, placing smaller producers at a cost disadvantage. At the same time, emerging-market dynamics are highly heterogeneous—offering high growth potential but also fragmenting competition and raising barriers to scale.
Response Strategies
To capitalize on the aforementioned opportunities and mitigate existing challenges, enterprises and relevant authorities should adopt the following strategic measures to ensure the concrete industry’s steady and sustainable growth:
Strengthen Technological Innovation and Digital Transformation
- Increase R&D Investment: Companies must allocate greater resources to research and development, focusing on state-of-the-art automation and digital-management systems.
- Implement Smart Production: By deploying intelligent equipment and IoT networks, firms can orchestrate end-to-end automation—from raw-material procurement and production scheduling to real-time quality monitoring.
- Foster Collaborative Innovation: Partnerships among industry, academia, and research institutions—or technology alliances—will accelerate the adoption and iteration of breakthrough solutions.
Build a Stable, Efficient Supply-Chain Ecosystem
- Secure Long-Term Supply Agreements: To hedge against raw-material price volatility, concrete producers should form strategic alliances or enter into multi-year contracts with cement and aggregate suppliers.
- Leverage Digital Supply-Chain Platforms: Real-time market intelligence, inventory management, and logistics optimization tools will help enterprises maintain uninterrupted input flows at controlled costs.
Proactively Embrace Environmental Policies and Green Production
- Upgrade to Low-Carbon Technologies: Firms must comply fully with tightening environmental regulations by retrofitting or replacing legacy equipment with energy-efficient, emissions-control, and water-reuse systems.
- Capture Policy Incentives: Through green-technology investments, companies can qualify for fiscal subsidies, tax credits, and “green factory” certifications, bolstering both profitability and brand reputation.
Pursue Differentiated Market Positioning and Brand Strategy
- Segment Product Offerings: Tailor portfolios to distinct regional or application-specific needs—for instance, high-performance, low-carbon mixes for premium markets versus cost-optimized, consistency-focused products for emerging economies.
- Elevate Brand and Service Excellence: Robust after-sales support, technical advisory services, and documented quality assurances will reinforce customer trust and expand market share.
Cultivate Talent and Upgrade Management Practices
- Develop a Skilled Workforce: Invest in in-house training programs and recruit specialists in digital systems, automation, and sustainable construction technologies.
- Establish Incentive Mechanisms: Flexible compensation and recognition frameworks can drive technology adoption, foster innovation, and enhance organizational agility in responding to market shifts.
This white paper has provided a comprehensive analysis of the concrete industry—covering market size, technological breakthroughs, competitive dynamics, regulatory landscapes, and the sector’s opportunities and challenges. The insights underscore that the industry stands at the threshold of a triple transformation: intelligent production, environmental sustainability, and global integration. By aligning strategies with these trends—through persistent R&D, agile management, and proactive policy compliance—enterprises can secure long-term resilience and growth.
Appendix
Data Sources and References
| Institution/Document Title | Data/Description | Author(s)/Affiliation | Publisher/Publishing Institution | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| International Cement Association (ICA) | Global concrete market CAGR of 3–4% expected over next 5 years | ICA | International Cement Association | 2024 |
| China Building Materials Federation (CBMF) | Smart equipment penetration >45% in new ready-mix concrete plants | CBMF | China Building Materials Federation | 2024 |
| U.S. Congress – Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) | $1.2 trillion allocated to infrastructure (bridges, highways, water, power) | U.S. Congress | United States Federal Government | 2021 |
| State Council of the People’s Republic of China – 14th Five-Year Plan | Focus on new urbanization, transportation powerhouse, and smart cities | PRC State Council | PRC State Council | 2021 |
| European Commission – Recovery and Resilience Facility (RRF) | Subsidies for high-performance, low-carbon concrete in green infrastructure | European Commission | European Union | 2020 |
| Government of Saudi Arabia – Vision 2030 | Vision 2030 drives large-scale urban developments (e.g., NEOM) and demand for high-temperature durable concrete | Saudi Government | Government of Saudi Arabia | 2016 |
| Government of India – National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) | China plans $1.5T infrastructure investment over the next decade | Ministry of Road Transport & Highways | Government of India | 2021 |
| ISO 22965 | Commercial concrete terminology, performance specs, and factory control standards | ISO | International Organization for Standardization | 2007 |
| EN 206 | Concrete classification, mix design, durability, and quality consistency | CEN | European Committee for Standardization | 2013 |
| ASTM C94 | Delivery standards, inspection protocols, and QC processes for commercial concrete | ASTM | ASTM International | 2019 |
| GB/T 14902 | Production quality standards and construction specifications for commercial concrete | SAC | Standardization Administration of China | 2018 |
| AS 1379 | Finished concrete quality management and third-party inspection mechanisms | Standards Australia | Standards Australia | 2007 |
| U.S. Green Building Council – LEED | Eco-friendliness and resource efficiency ratings for concrete applications | USGBC | US Green Building Council | 2000 |
| Building Research Establishment – BREEAM | Whole-life cycle environmental impact assessment for building materials | BRE | Building Research Establishment | 1990 |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development (MOHURD) | China Green Building Material Certification star-rating system | MOHURD | Ministry of Housing & Urban-Rural Development | 2014 |
| EPD International – Environmental Product Declaration | Transparent disclosure of product carbon footprint | EPD International | Global EPD Programme | 2012 |
| China Academy of Building Research | Construction waste micronization activation tech boosts recycled aggregate concrete strength to C50, cuts cost by 30% | China Academy of Building Research | China Academy of Building Research | 2023 |
| University of Science and Technology Beijing | CO₂ mineralization curing in Xiong’an New Area reduces concrete carbon footprint by 21kg/m³ | USTB | University of Science & Technology Beijing | 2022 |
| Heidelberg Materials (HeidelbergCement) | World’s first concrete kiln CCUS project sequesters 100k tons CO₂/year | Heidelberg Materials | HeidelbergCement | 2023 |
| CNBM & Conch Cement | Calcium carbide slag replacing limestone cuts clinker emissions below 350kg/ton | CNBM & Conch Cement | CNBM / Conch Cement | 2024 |
| SAP | End-to-end SCM system for concrete production improves inventory turnover by 25% | SAP | SAP SE | 2022 |
| Glodon | BIM quantity software holds 41% market share, shortens settlement cycles by 40% | Glodon | Glodon | 2023 |
| Siemens | Industry-leading PLC and automated pumping systems | Siemens | Siemens AG | 2023 |
| Huawei & CSCEC West Construction | BIM+5G collaboration platform reduces design changes by 30% | Huawei & CSCEC West Construction | Huawei Technologies | 2023 |
| HBC Radiomatic | Wireless remote control enables precise concrete pump boom operation | HBC Radiomatic | HBC Radiomatic | 2022 |
| MX3D (Netherlands) | 3D-printed recycled aggregate bridges cut material waste by 60%, costs by 30% | MX3D | MX3D | 2023 |
| Shanghai Construction Group | UHPC-RC composite beams shorten construction time by 50%, win National Tech Progress Award | Shanghai Construction Group | Shanghai Construction Group | 2022 |
| VICON (Netherlands) | Nano-enhanced industrial waste blends improve compressive strength by 20% | VICON | VICON | 2023 |
| European Concrete Association (ECA) | Shared low-carbon concrete patents cut carbon capture costs by 30% | ECA | European Concrete Association | 2021 |
Industry Terminology Definitions
To aid reader comprehension of the specialized content in this white paper, key industry terms are defined as follows:
- Concrete: A construction material produced by proportionally mixing cement, sand, aggregates, and water; used for foundations, structures, and pavements.
- Concrete Industry: The sector encompassing the full value chain of concrete production, distribution, and associated equipment manufacturing.
- Concrete Batching Plant: A facility or set of equipment that measures, mixes, and produces concrete by combining raw materials in prescribed proportions.
- Ready-Mix Concrete: Concrete that is mixed to specification at a central plant and then transported to the construction site, offering controlled production processes and consistent quality.
- Cement: The primary binding agent in concrete, manufactured by grinding clinker; its market price fluctuations directly impact overall concrete production costs.
- Smart Production Equipment: Machinery that incorporates automation, digital monitoring, and advanced control systems to enhance production efficiency, reduce energy use, and ensure consistent product quality.
- Green Building: A construction approach that prioritizes energy savings, environmental protection, efficient resource use, and ecological stewardship throughout a building’s life cycle, often requiring low-carbon materials and processes.
- Supply-Chain Integration: A strategic practice of collaborating across upstream raw-material suppliers, midstream producers, and downstream construction firms to share resources, lower costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.


